Emilia: An Extensive, Multilingual, and Diverse Speech Dataset for Large-Scale Speech Generation
Abstract
Recent advancements in speech generation models have been significantly driven by the use of large-scale
training data. However, producing highly spontaneous, human-like speech remains a challenge due to the
scarcity of large, diverse, and spontaneous speech datasets. In response, we introduce Emilia,
the first
large-scale, multilingual, and diverse speech generation dataset. Emilia starts with over 101k hours of
speech across six languages, covering a wide range of speaking styles to enable more natural and spontaneous
speech generation. To facilitate the scale-up of Emilia, we also present Emilia-Pipe, the first
open-source
preprocessing pipeline designed to efficiently transform raw, in-the-wild speech data into high-quality
training data with speech annotations. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of both Emilia and
Emilia-Pipe. Demos are available at: https://emilia-dataset.github.io/Emilia-Demo-Page/.
The Emilia Dataset
Overview
The Emilia dataset is constructed from a vast collection of speech data sourced from diverse
video platforms and podcasts on the Internet, covering various content genres such as talk shows, interviews,
debates, sports commentary, and audiobooks. This variety ensures the dataset captures a wide array of real
human speaking styles. The initial version of the Emilia dataset includes a total of 101,654 hours of
multilingual speech data in six different languages: English, French, German, Chinese, Japanese, and Korean.
The table and chart below provide the duration statistics for each language in the dataset.
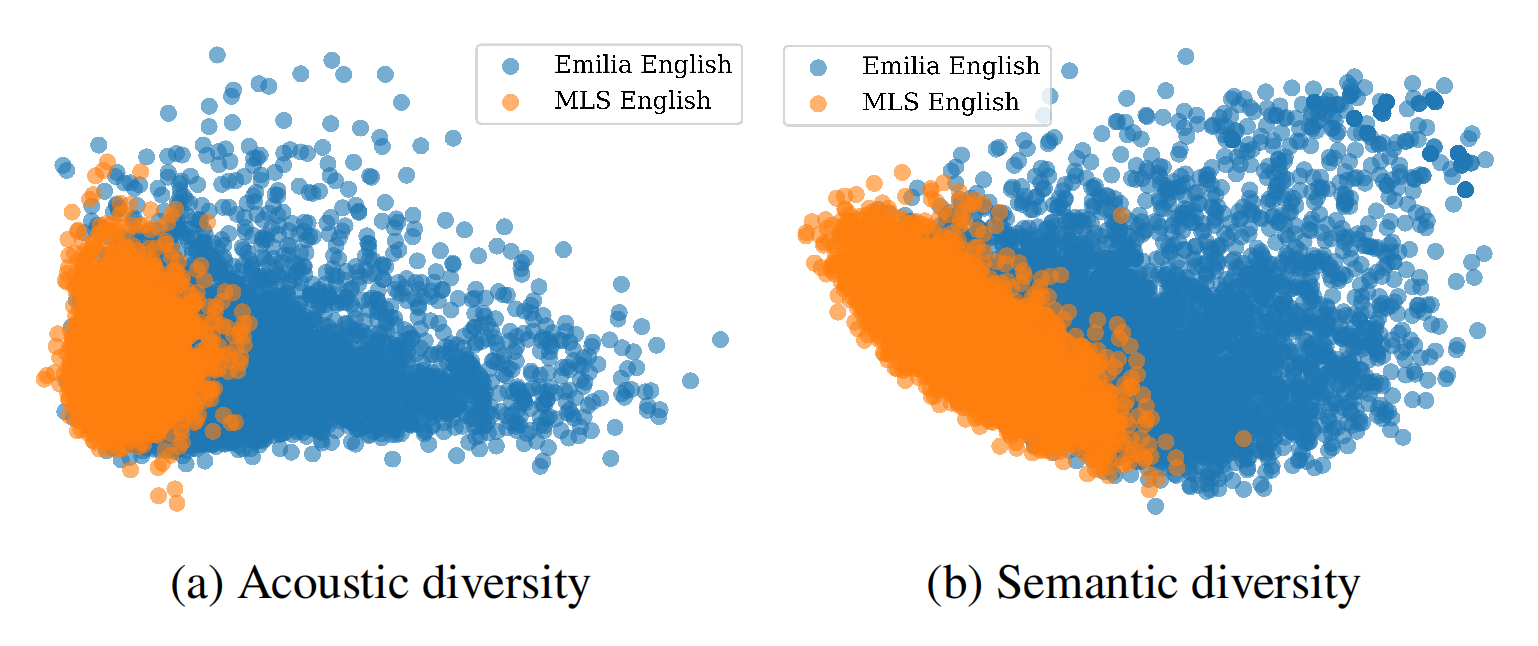
The figure below compares the acoustic and semantic diversities between Emilia and MLS datasets, which is sourced from audiobooks. The more scattered pattern highlights the Emilia dataset as encompassing a richer acoustic characteristic and semantic coverage compared to the existing audiobook dataset.
Data Preview
To better understand the performance of the pipeline as well as the diversity and quality of the dataset, we have sampled a few speech examples below for preview.
The Emilia-Pipe Preprocessing Pipeline
Emilia-Pipe is the first open-source preprocessing pipeline designed to transform in-the-wild
speech data into high-quality training data with annotations for speech generation. It consists of six major
steps: Standardization, Source Separation, Speaker Diarization, Fine-grained Segmentation by VAD, ASR, and
Filtering. The figure below provides an overview of the Emilia-Pipe.
After processing, the Emilia-Pipe outputs the speech data in JSON and MP3 format. The JSON file contains metadata such as language, and transcription, while the MP3 file contains the speech data. The JSON file is structured as follows:
Demos
In this section, we demonstrate the zero-shot TTS performance of the models (Soundstorm and VoiceBox) trained on Emilia.




